Understanding the Importance of Rain Protection in Bus Shelters
Bus shelters play an essential role in urban infrastructure, providing comfort and protection for passengers during different weather conditions. Among all environmental challenges, rain poses one of the most common and disruptive factors. A poorly designed shelter can leave commuters drenched, create slippery surfaces, and diminish the usability of public transport systems. Enhancing the rain protection of bus shelters is not only a matter of comfort but also of safety and design efficiency.
Optimizing Roof Design for Maximum Coverage
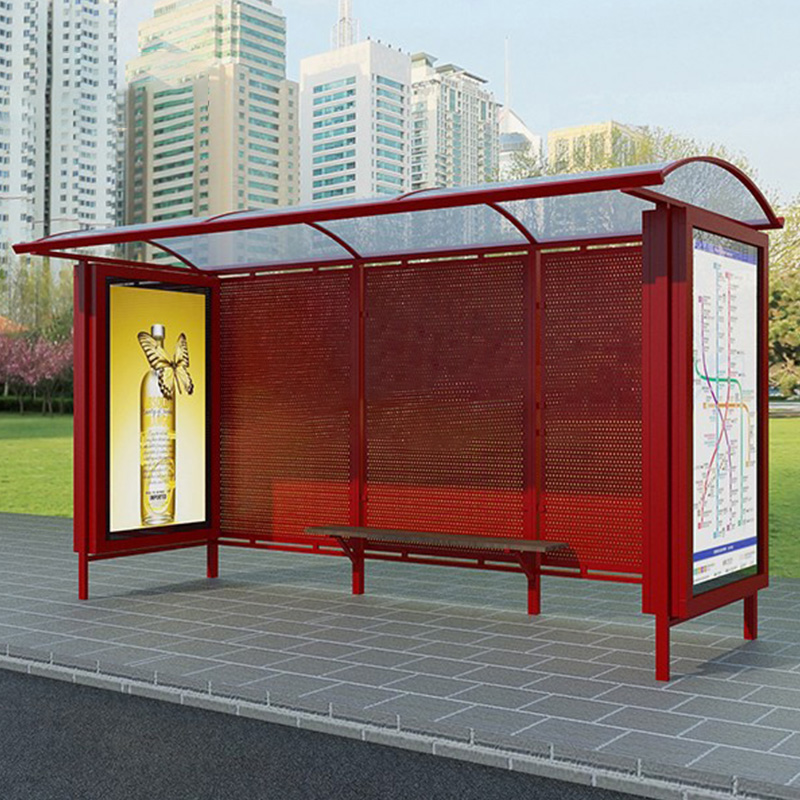
The roof is the first line of defense against rain, and its design directly affects the shelter’s protective efficiency. A properly engineered roof should divert rainwater away from the seating and standing areas. Key design considerations include slope, overhang length, and material selection.
Roof Shape and Angle
A sloped or arched roof allows rainwater to flow quickly toward the edges, minimizing pooling and leakage. The optimal angle depends on the average rainfall of the area, but typically, a slope of 10–15 degrees provides effective drainage while maintaining an aesthetic profile.
Extended Overhangs
Longer roof overhangs can help prevent rain from entering the seating zone, particularly when wind is blowing rain sideways. However, excessive overhangs may require stronger support structures, so a balance between coverage and stability is crucial.
Durable and Water-Resistant Materials
Materials like polycarbonate sheets, tempered glass with hydrophobic coating, or aluminum composite panels are excellent for rain resistance. Polycarbonate, for instance, offers transparency, UV resistance, and long-term durability against corrosion and leakage.
Improving Drainage Systems for Better Water Management
An effective drainage system ensures that rainwater is quickly channeled away from the shelter structure, preventing puddles and structural damage. Integrating advanced drainage solutions not only protects users but also prolongs the shelter’s lifespan.
Gutter and Downspout Integration
A combination of gutters along roof edges and downspouts that lead water to designated drainage points keeps the shelter dry and functional. These systems should be made from corrosion-resistant materials such as stainless steel or PVC and be easy to clean.
Ground-Level Drainage Design
Proper slope design around the shelter ensures that water flows away naturally. In high-rainfall regions, integrating underground drainage channels or perforated ground grates can further improve efficiency.
Enhancing Side Protection from Wind-Driven Rain
Rain protection isn’t just about what’s above—side panels play a major role in shielding commuters from angled or wind-driven rain. Incorporating partial or full enclosures significantly enhances comfort and usability during storms.
Side Panel Configurations
Adding transparent or frosted glass side panels on at least two sides of the shelter provides a protective barrier against crosswinds. Transparent materials maintain visibility and a sense of openness, while still blocking moisture.
Weather Sealing
Sealing the joints between panels and roof sections using silicone or rubber gaskets helps prevent leaks. These seals must be UV-resistant to ensure long-term effectiveness under outdoor conditions.
Using Advanced Materials for Weather Resistance
Material innovation plays a crucial role in improving rain protection. Modern shelters increasingly rely on advanced composites and coatings to repel water, reduce corrosion, and simplify maintenance.
| Material | Advantages |
| Polycarbonate Panels | Lightweight, impact-resistant, UV-stable, easy to clean |
| Aluminum Composite | Corrosion-resistant, customizable color finishes, strong support |
| Tempered Glass | Elegant appearance, wind-resistant, hydrophobic coating options |
Maintaining the Shelter for Continuous Protection
Even a perfectly designed bus shelter requires regular maintenance to sustain its rain protection performance. Neglected structures often develop leaks, clogged drains, or degraded seals that compromise their effectiveness.
- Clean roofs and gutters regularly to prevent blockages from debris.
- Inspect seals and joints after heavy rain to detect leaks early.
- Reapply hydrophobic coatings annually for maximum water repellency.
- Replace corroded or damaged metal components promptly.
Integrating Smart Design and User Experience
Modern urban design increasingly integrates technology into bus shelters. Smart shelters equipped with sensors and data analytics can detect water accumulation and trigger maintenance alerts automatically. Additionally, thoughtful ergonomic design—such as raised seating platforms or anti-slip flooring—ensures that commuters remain comfortable and safe during wet weather.
Ultimately, enhancing rain protection in bus shelters is not only an engineering task but also a commitment to improving the passenger experience. Combining efficient roof designs, smart materials, reliable drainage, and consistent maintenance ensures that bus shelters remain dry, durable, and welcoming to all users, regardless of the weather.



 English
English Español
Español