Introduction: The Need for Weather Protection in Bus Shelters
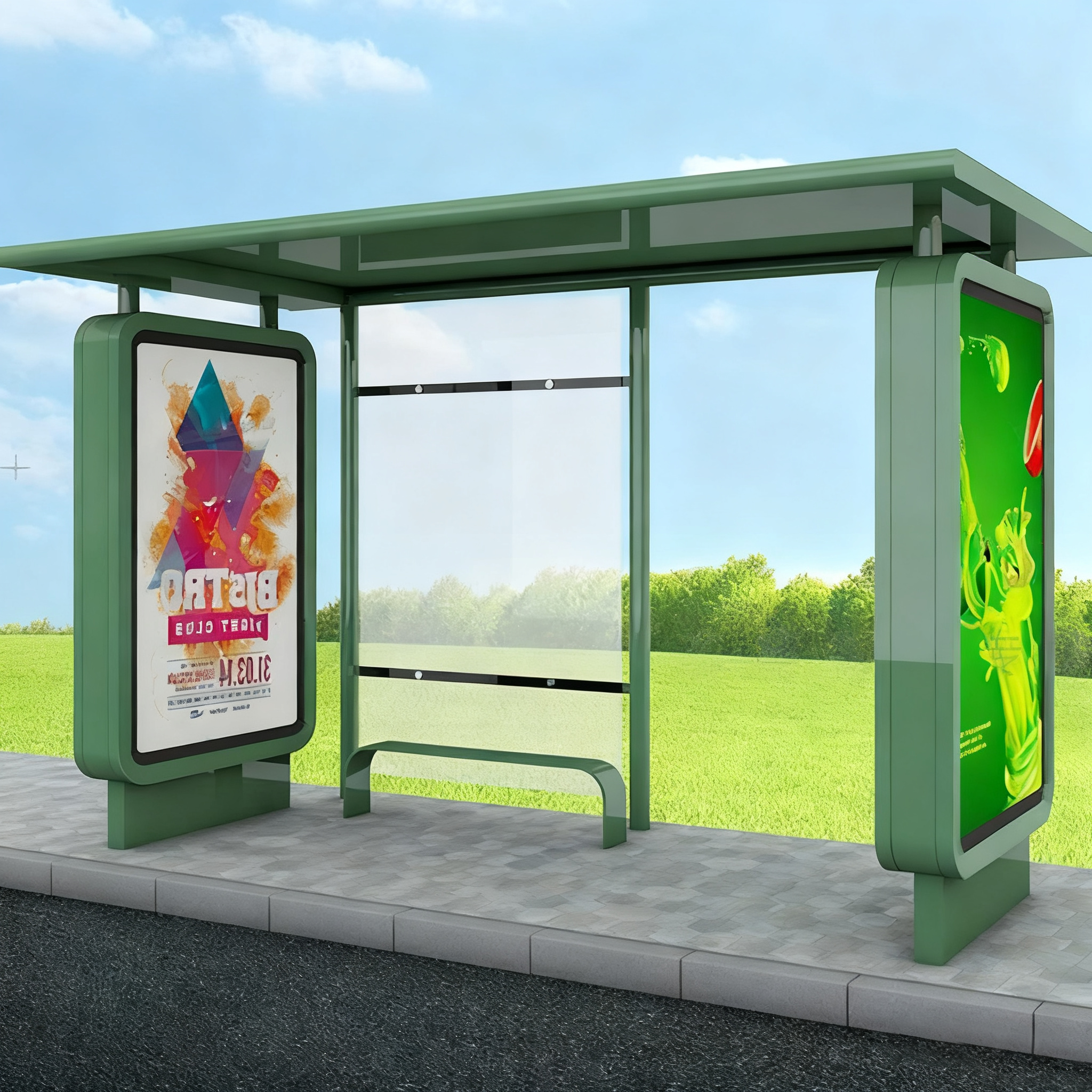
Bus shelters serve as a vital refuge for passengers waiting for public transportation. In areas with harsh weather conditions, the ability of a bus shelter to protect passengers from extreme weather is crucial for their comfort and safety. Extreme weather conditions, such as heavy rainfall, snow, intense heat, and strong winds, can make waiting for a bus uncomfortable and even dangerous. This article explores how well modern bus shelters protect against these challenging weather elements.
Protection Against Rain and Snow
Rain and snow are common weather conditions that can disrupt the comfort of bus passengers. Bus shelters are designed with specific features that provide adequate protection from precipitation, ensuring that passengers stay dry and safe while waiting for their ride.
Roof Design and Materials
The roof of a bus shelter is one of its primary protective elements against rain and snow. Modern shelters often feature sloped or curved roofs made from durable, weather-resistant materials such as:
- Polycarbonate or Acrylic Panels: These transparent materials allow light to filter through while providing protection from rain and snow.
- Metal Roofs: Steel or aluminum roofs are commonly used in bus shelters because they are resistant to corrosion and can withstand heavy snowfall and rain.
- Green Roofs: Some modern shelters feature living roofs with vegetation, which not only help with weather protection but also contribute to the environment by reducing urban heat islands.
Side Walls and Enclosures
In addition to the roof, side walls play a crucial role in protecting passengers from wind-driven rain and snow. Bus shelters often feature:
- Tempered Glass Panels: These provide clear visibility while also acting as a barrier to the elements, keeping rain and snow at bay.
- Polycarbonate Sheets: These are lightweight, impact-resistant materials that provide weather protection while being less likely to shatter than glass.
- Retractable Screens: Some shelters are equipped with retractable or roll-up screens, which can be lowered during adverse weather conditions to provide additional protection.
Protection Against Wind
Wind is another challenging element that bus shelters must address, especially in coastal or open areas where gusts can be particularly strong. The design and placement of bus shelters play a critical role in protecting passengers from wind.
Shelter Structure and Orientation
The structure of the shelter, including its height, shape, and orientation, can significantly influence its ability to shield passengers from strong winds:
- Enclosed Shelters: Fully enclosed shelters with solid walls on three or more sides provide substantial wind protection. The more enclosed the structure, the more effective it is at blocking wind.
- Strategic Placement: Shelters that are placed with consideration of prevailing wind directions can reduce the wind exposure for passengers waiting inside.
- Windbreak Panels: Some shelters incorporate additional windbreak panels along the sides or at the entrance to deflect gusts and ensure passenger comfort.
Wind-Resistant Materials
The materials used in bus shelters also affect their ability to withstand strong winds. Some features include:
- Reinforced Frames: The framework of bus shelters is often made from steel or aluminum, which are both sturdy and capable of resisting wind forces.
- Aerodynamic Designs: Some shelters feature rounded edges or sloping sides to minimize wind resistance and prevent the structure from being destabilized during strong gusts.
Protection Against Extreme Heat
In areas where temperatures can reach extreme highs, such as in desert or tropical regions, bus shelters are designed to provide shade and cooling to ensure passenger comfort.
Shading and Cooling Features
Bus shelters in hot climates often incorporate materials and design elements that help reduce the buildup of heat inside the shelter:
- Reflective Coatings: Some shelters feature reflective coatings on the roof or sides to deflect sunlight and reduce heat absorption.
- Ventilation Systems: To enhance airflow and reduce temperature buildup, some shelters are equipped with ventilation openings or cooling systems that allow hot air to escape.
- Green Roofs: As mentioned earlier, green roofs not only protect against rain and snow but also help cool the air around the shelter by providing natural insulation and reducing the heat island effect.
Heat-Resistant Materials
Materials that do not absorb excessive heat are also important for shelters in hot climates. Common heat-resistant materials include:
- Heat-Reflective Glass: Glass panels with heat-reflective coatings can reduce the amount of heat transferred into the shelter.
- Aluminum and Stainless Steel: These metals are often used in the structure and roofing of bus shelters as they resist heat buildup and offer durability in extreme temperatures.
Conclusion: Creating Comfortable and Safe Bus Shelters
Bus shelters are essential for providing shelter and comfort to passengers, especially during extreme weather conditions. Through smart design, the use of durable materials, and thoughtful placement, modern bus shelters effectively protect passengers from rain, snow, wind, and extreme heat. By continuing to innovate and improve these shelters, cities can ensure that public transportation is more comfortable and accessible, no matter the weather.



 English
English Español
Español