The Importance of Industrial Guardrails in Workplace Safety
Industrial guardrails are a critical component of safety infrastructure in manufacturing plants, warehouses, and high-traffic industrial environments. By providing physical barriers around machinery, walkways, and hazardous zones, guardrails reduce the risk of accidents, protect personnel, and safeguard valuable equipment. Their presence is not only a matter of practical safety but also a legal requirement in many jurisdictions to comply with occupational health and safety regulations.
As industries adopt automation and heavy machinery, the need for reliable protective barriers has grown. Guardrails serve as a first line of defense against collisions, slips, and falls, contributing to both operational safety and regulatory compliance.
Meeting Regulatory Standards with Guardrails
Industrial safety regulations often mandate the installation of guardrails to protect employees from hazards associated with machinery, elevated platforms, and material handling operations. Standards such as OSHA in the United States, ISO 14122 for machinery access, and EN 13374 in Europe specify the height, strength, and positioning of guardrails to ensure maximum protection.
Compliance requires selecting guardrails that meet these specifications and maintaining them in good condition. Failing to implement compliant guardrails can result in legal penalties, increased liability, and heightened risk of workplace accidents.
Types of Industrial Guardrails and Their Applications
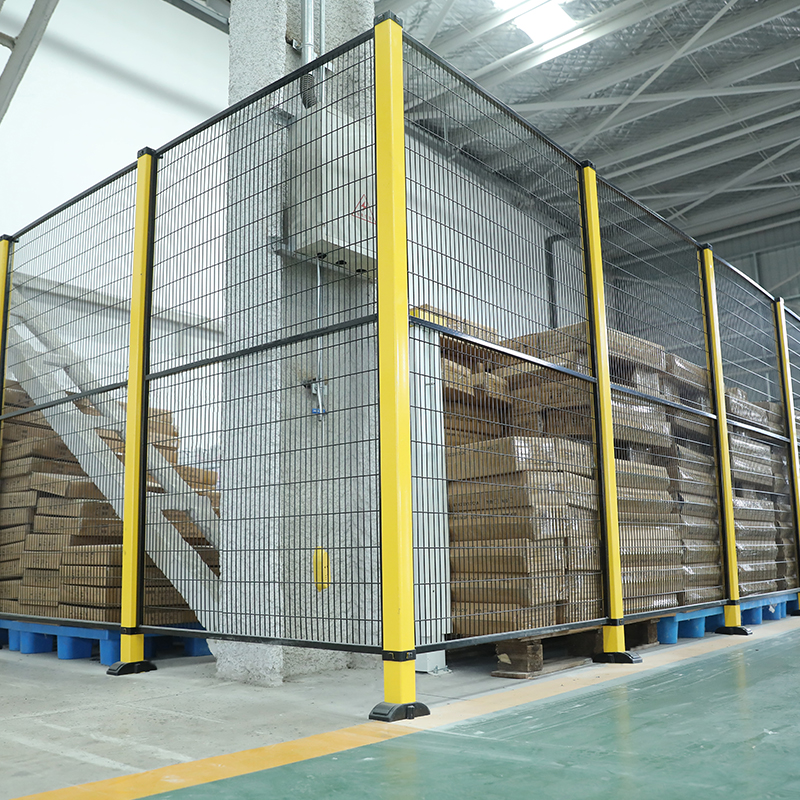
Industrial guardrails come in various types, each designed for specific applications. Standard fixed guardrails are used to protect walkways, platforms, and workstations. Modular and removable guardrails provide flexibility for dynamic environments where layout changes frequently. Heavy-duty steel guardrails are ideal for areas with vehicle traffic, such as forklift lanes, while low-impact plastic or composite guardrails are suitable for pedestrian zones.
Common Guardrail Types
- Fixed steel guardrails for permanent installations
- Modular guardrails for flexible and reconfigurable spaces
- Plastic or composite guardrails for low-impact pedestrian protection
- Vehicle-rated guardrails for forklift and machinery lanes
Enhancing Safety Through Strategic Placement
Proper installation and placement of guardrails are essential for maximizing their effectiveness. Guardrails should be positioned to prevent access to hazardous areas, guide pedestrian traffic, and separate machinery from walkways. Strategic placement reduces the likelihood of collisions and accidents while optimizing workflow efficiency.
Regular inspection and maintenance of guardrails ensure they remain robust and compliant. Damaged or loose guardrails can compromise safety and result in regulatory violations.
Balancing Safety and Operational Efficiency
While guardrails are primarily a safety measure, their design can impact operational efficiency. Modern guardrail systems offer features such as modular sections, gates, and removable panels to maintain workflow flexibility without compromising safety. By incorporating these features, companies can meet regulatory requirements while ensuring minimal disruption to daily operations.
Additionally, integrating guardrails with other safety measures, such as floor markings, signage, and automated barriers, creates a comprehensive safety ecosystem that supports both compliance and productivity.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Industrial Guardrails
Investing in high-quality industrial guardrails provides a significant return by reducing workplace injuries, lowering liability risks, and minimizing equipment damage. While initial installation costs may vary based on materials and complexity, the long-term benefits outweigh the upfront investment.
Companies that prioritize guardrail installation experience fewer accidents, lower insurance premiums, and enhanced employee confidence, all of which contribute to operational efficiency and cost savings.
Guardrail Cost Considerations
- Material type: steel, aluminum, or composite
- Installation complexity and labor costs
- Maintenance and inspection frequency
Integrating Guardrails Into Safety Programs
Guardrails are most effective when integrated into broader workplace safety programs. This includes training employees on safe navigation around guardrails, understanding their purpose, and responding appropriately in case of emergency situations. Combining physical barriers with safety protocols enhances compliance with regulatory standards and promotes a culture of safety.
Safety programs that incorporate guardrail inspections, reporting systems, and incident analysis help organizations continually improve workplace safety and ensure that guardrails remain functional and effective over time.
Comparing Guardrail Types and Compliance Features
| Feature | Standard Guardrail | Advanced Guardrail |
| Material Strength | Moderate | High, impact-resistant |
| Adjustability | Fixed | Modular and reconfigurable |
| Compliance Assurance | Basic | Meets multiple regulatory standards |
Conclusion: Guardrails as a Compliance Necessity
Industrial guardrails are essential not only for protecting workers and equipment but also for meeting legal safety requirements. Their correct selection, installation, and integration into broader safety programs ensure that workplaces remain compliant, efficient, and secure. Companies that invest in robust guardrail systems demonstrate a commitment to employee safety, regulatory compliance, and long-term operational success.
Ultimately, guardrails serve as a physical manifestation of an organization's safety culture. They prevent accidents, enhance productivity, and provide peace of mind, making them indispensable in modern industrial environments.



 English
English Español
Español